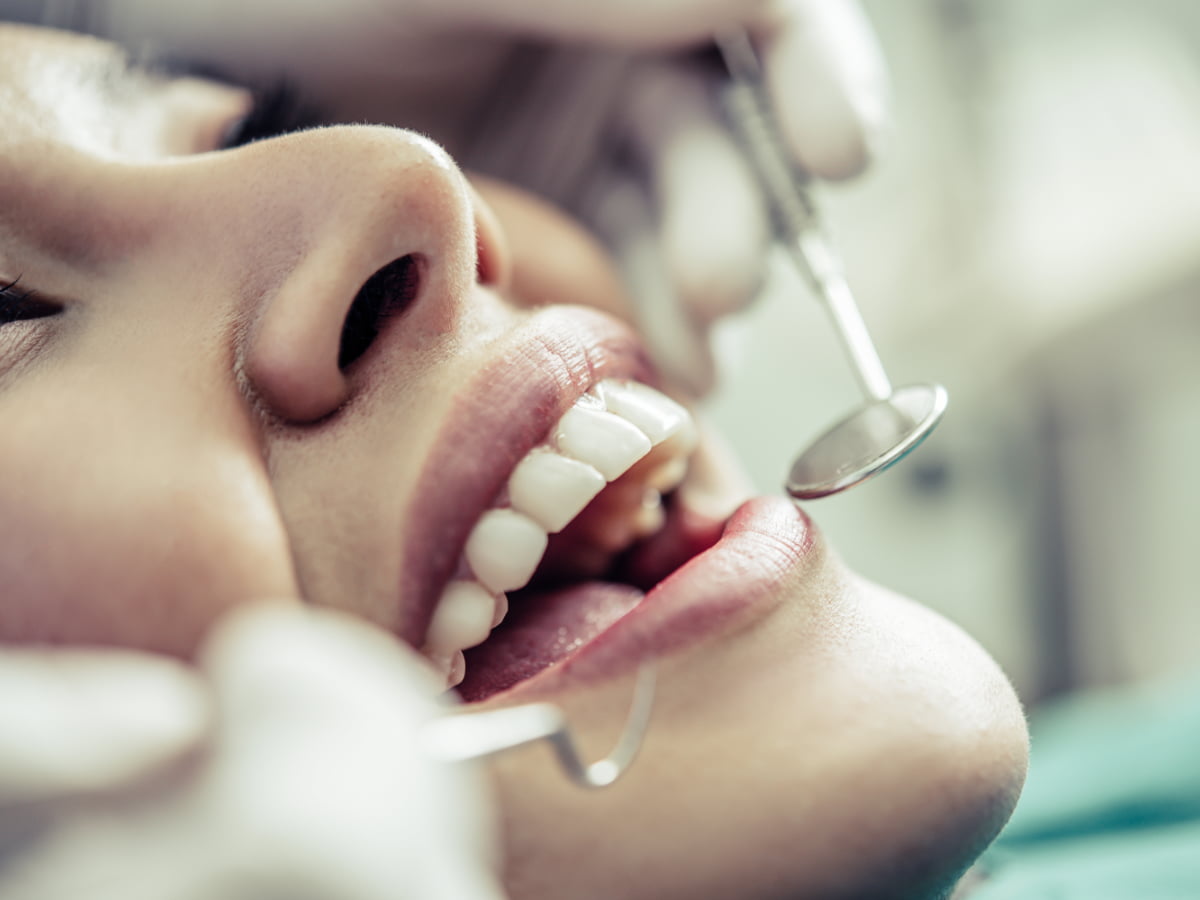
Clinical examination of teeth — Your dentist will check for signs of tooth decay by examining the surface of every tooth. They will also check for any problems with fillings, braces, bridges, dentures, crowns, or other restorations.
Gum tissue – Your dentist will examine your gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Your dentist will look for signs of gum disease, which include red or puffy gum tissue and tissue that easily bleeds when gently poked.
Soft tissue — The soft tissues of your mouth include the tongue, inside of the lips and cheeks, and the floor and roof of the mouth. Your dentist will examine these areas for spots, lesions, cuts, swellings, or growths that could indicate an oral health problem. Your dentist will also inspect the back of your throat and tonsil area.
Head and neck — Your dentist will look for any problems on the exterior surface of your head and neck, as well as feel for any swelling or tenderness (which are signs of an infection or disease) in your lymph nodes and salivary glands in your neck area. Your dentist will also examine your temporomandibular joint to determine if it is working properly.
Occlusion — Your dentist will check how well your upper and lower teeth come together. Your dentist might simply look at how your teeth meet, or he or she might take wax impressions of your teeth if a more careful exam of “your bite” is necessary.
X-rays — Your dentist will take X-rays (Bite Wings) to look for signs of tooth decay, as well as for gum disease and other oral health problems.